The concept of the afterlife changed in different eras of Egypt's very long history, but for the most part, it was imagined as a paradise where one lived eternally. To the Egyptians, their country was the most perfect place which had been created by the gods for human happiness.
The afterlife, therefore, was a mirror image of the life one had lived on earth - down to the last detail - with the only difference being an absence of all those aspects of existence one found unpleasant or sorrowful. One inscription about the afterlife talks about the soul being able to eternally walk beside its favorite stream and sit under its favorite sycamore tree, others show husbands and wives meeting again in paradise and doing all the things they did on earth such as plowing the fields, harvesting the grain, eating and drinking.

In order to enjoy this paradise, however, one would need the same items one had during one's life. Tombs and even simple graves included personal belongings as well as food and drink for the soul in the afterlife. These items are known as 'grave goods' and have become an important resource for modern-day archaeologists in identifying the owners of tombs, dating them, and understanding Egyptian history. Although some people object to this practice as 'grave robbing,' the archaeologists who professionally excavate tombs are assuring the deceased of their primary objective: to live forever and have their name remembered eternally. According to the ancient Egyptians' own beliefs, the grave goods placed in the tomb would have performed their function many centuries ago.
Food, Drink & Shabti Dolls
Grave goods, in greater or lesser number and varying worth, have been found in almost every Egyptian grave or tomb which was not looted in antiquity. The articles one would find in a wealthy person's tomb would be similar to those considered valuable today: ornately crafted objects of gold and silver, board games of fine wood and precious stone, carefully wrought beds, chests, chairs, statuary, and clothing. The finest example of a pharaoh's tomb, of course, is King Tutankhamun's from the 14th century BCE discovered by Howard Carter in 1922 CE, but there have been many tombs excavated throughout ancient Egypt which make clear the social status of the individual buried there. Even those of modest means included some grave goods with the deceased.
The primary purpose of grave goods, though, was not so show off the deceased person's status but to provide the dead with what they would need in the afterlife. A wealthy person's tomb, therefore, would have more grave goods - of whatever that person favored in life - than a poorer person. Favorite foods were left in the tomb such as bread and cake, but food and drink offerings were expected to be made by one's survivors daily.
In the tombs of the upper-class nobles and royalty an offerings chapel was included which featured the offerings table. One's family would bring food and drink to the chapel and leave it on the table. The soul of the deceased would supernaturally absorb the nutrients from the offerings and then return to the afterlife. This ensured one's continual remembrance by the living and so one's immortality in the next life.
If a family was too busy to tend to the daily offerings and could afford it, a priest (known as the ka-priest or water-pourer) would be hired to perform the rituals. However the offerings were made, though, they had to be taken care of on a daily basis. The famous story of Khonsemhab and the Ghost (dated to the New Kingdom of Egypt c. 1570-1069 BCE) deals with this precise situation.
In the story, the ghost of Nebusemekh returns to complain to Khonsemhab, high priest of Amun, that his tomb has fallen into disrepair and he has been forgotten so that offerings are no longer brought. Khonsemhab finds and repairs the tomb and also promises that he will make sure offerings are provided from then on. The end of the manuscript is lost, but it is presumed the story ends happily for the ghost of Nebusemekh. If a family should forget their duties to the soul of the deceased, then they, like Khonsemhab, could expect to be haunted until this wrong was righted and regular food and drink offerings reinstated.
Beer was the drink commonly provided with grave goods. In Egypt, beer was the most popular beverage - considered the drink of the gods and one of their greatest gifts - and was a staple of the Egyptian diet. A wealthy person (such as Tutankhamun) was buried with jugs of freshly brewed beer whereas a poorer person would not be able to afford that kind of luxury. People were often paid in beer so to bury a jug of it with a loved one would be comparable to someone today burying their paycheck.
Beer was sometimes brewed specifically for a funeral, since it would be ready, from inception to finish, by the time the corpse had gone through the mummification process. After the funeral, once the tomb had been closed, the mourners would have a banquet in honor of the dead person's passing from time to eternity, and the same brew which had been made for the deceased would be enjoyed by the guests; thus providing communion between the living and the dead.
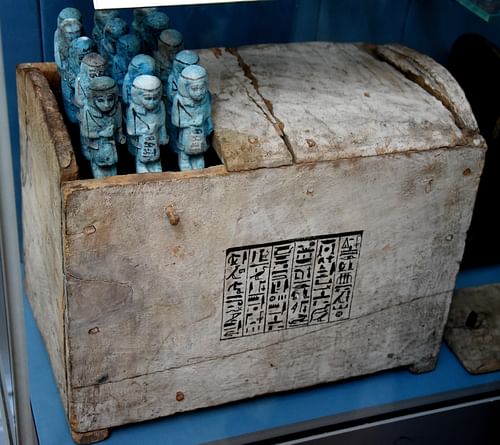
Among the most important grave goods was the shabti doll. Shabti were made of wood, stone, or faience and often were sculpted in the likeness of the deceased. In life, people were often called upon to perform tasks for the king, such as supervising or laboring on great monuments, and could only avoid this duty if they found someone willing to take their place. Even so, one could not expect to shirk one's duties year after year, and so a person would need a good excuse as well as a replacement worker.
Since the afterlife was simply a continuation of the present one, people expected to be called on to do work for Osiris in the afterlife just as they had labored for the king. The shabti doll could be animated, once one had passed into the Field of Reeds, to assume one's responsibilities. The soul of the deceased could continue to enjoy a good book or go fishing while the shabti took care of whatever work needed to be done. Just as one could not avoid one's obligations on earth, though, the shabti could not be used perpetually. A shabti doll was good for only one use per year. People would commission as many shabti as they could afford in order to provide them with more leisure in the afterlife.
Shabti dolls are included in graves throughout the length of Egypt's history. In the First Intermediate Period (2181-2040 BCE) they were mass-produced, as many items were, and more are included in tombs and graves of every social class from then on. The poorest people, of course, could not even afford a generic shabti doll, but anyone who could, would pay to have as many as possible. A collection of shabtis, one for each day of the year, would be placed in the tomb in a special shabti box which was usually painted and sometimes ornamented.
Religious Texts & Judgment by Osiris
Instructions on how one would animate a shabti in the next life, as well as how to navigate the realm which waited after death, was provided through the texts inscribed on tomb walls and, later, written on papyrus scrolls. These are the works known today as the Pyramid Texts (c. 2400-2300 BCE), the Coffin Texts (c. 2134-2040 BCE), and The Egyptian Book of the Dead (c. 1550-1070 BCE). The Pyramid Texts are the oldest religious texts and were written on the walls of the tomb to provide the deceased with assurance and direction.
When a person's body finally failed them, the soul would at first feel trapped and confused. The rituals involved in mummification prepared the soul for the transition from life to death, but the soul could not depart until a proper funeral ceremony was observed. When the soul woke in the tomb and rose from its body, it would have no idea where it was or what had happened. In order to reassure and guide the deceased, the Pyramid Texts and, later, Coffin Texts were inscribed and painted on the inside of tombs so that when the soul awoke in the dead body it would know where it was and where it now had to go.
These texts eventually turned into The Egyptian Book of the Dead (whose actual title is The Book of Coming Forth by Day), which is a series of spells the dead person would need in order to navigate through the afterlife. Spell 6 from the Book of the Dead is a rewording of Spell 472 of the Coffin Texts, instructing the soul in how to animate the shabti. Once the person died and then the soul awoke in the tomb, that soul was led - usually by the god Anubis but sometimes by others - to the Hall of Truth (also known as The Hall of Two Truths) where it was judged by the great god Osiris.
The soul would then speak the Negative Confession (a list of 'sins' they could honestly say they had not committed such as 'I have not lied, I have not stolen, I have not purposefully made another cry'), and then the heart of the soul would be weighed on a scale against the white feather of ma'at, the principle of harmony and balance.
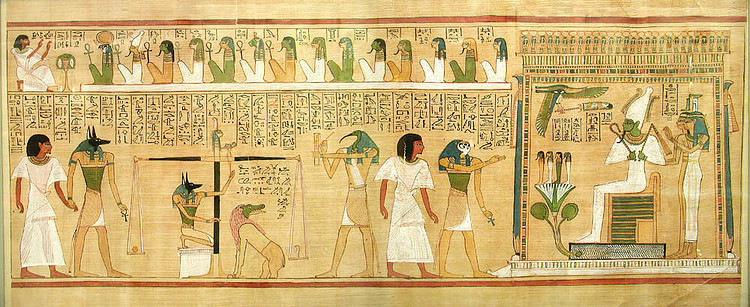
If the heart was found to be lighter than the feather, then the soul was considered justified; if the heart was heavier than the feather, it was dropped onto the floor where it was eaten up by the monster Amut, and the soul would then cease to exist. There was no 'hell' for eternal punishment of the soul in ancient Egypt; their greatest fear was non-existence, and that was the fate of someone who had done evil or had purposefully failed to do good.
If the soul was justified by Osiris then it went on its way. In some eras of Egypt, it was believed the soul then encountered various traps and difficulties which they would need the spells from The Book of the Dead to get through. In most eras, though, the soul left the Hall of Truth and traveled to the shores of Lily Lake (also known as The Lake of Flowers) where they would encounter the perpetually unpleasant ferryman known as Hraf-hef ("He Who Looks Behind Himself") who would row the soul across the lake to the paradise of the Field of Reeds. Hraf-hef was the 'final test' because the soul had to find some way to be polite, forgiving, and pleasant to this very unpleasant person in order to cross.
Once across the lake, the soul would find itself in a paradise which was the mirror image of life on earth, except lacking any disappointment, sickness, loss, or - of course - death. In The Field of Reeds the soul would find the spirits of those they had loved and had died before them, their favorite pet, their favorite house, tree, stream they used to walk beside - everything one thought one had lost was returned, and, further, one lived on eternally in the direct presence of the gods.
Pets & the Afterlife
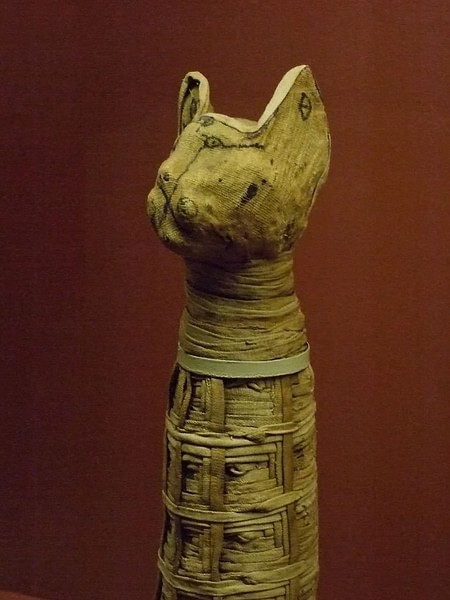
Reuniting with loved ones and living eternally with the gods was the hope of the afterlife but equally so was being met by one's favorite pets in paradise. Pets were sometimes buried in their own tombs but, usually, with their master or mistress. If one had enough money, one could have one's pet cat, dog, gazelle, bird, fish, or baboon mummified and buried alongside one's corpse. The two best examples of this are High Priestess Maatkare Mutemhat (c. 1077-943 BCE) who was buried with her mummified pet monkey and the Queen Isiemkheb (c. 1069-943 BCE) who was buried with her pet gazelle.
Mummification was expensive, however, and especially the kind practiced on these two animals. They received top treatment in their mummification and this, of course, represented the wealth of their owners. There were three levels of mummification available: top-of-the-line where one was treated as a king (and received a burial in keeping with the glory of the god Osiris); middle-grade where one was treated well but not that well; and the cheapest where one received minimal service in mummification and burial. Still, everyone - rich or poor - provided their dead with some kind of preparation of the corpse and grave goods for the afterlife.
Pets were treated very well in ancient Egypt and were represented in tomb paintings and grave goods such as dog collars. The tomb of Tutankhamun contained dog collars of gold and paintings of his hunting hounds. Although modern day writers often claim that Tutankhamun's favorite dog was named Abuwtiyuw, who was buried with him, this is not correct. Abuwtiyuw is the name of a dog from the Old Kingdom of Egypt who so pleased the king that he was given private burial and all the rites due a person of noble birth. The identity of the king who loved the dog is unknown, but the dog of king Khufu (2589-2566 BCE), Akbaru, was greatly admired by his master and buried with him.
The collars of dogs, which frequently gave their name, often were included as grave goods. The tomb of the noble Maiherpre, a warrior who lived under the reign of Thutmose III (1458-1425 BCE) contained two ornamented dog collars of leather. These were dyed pink and decorated with images. One of them has horses and lotus flowers punctuated by brass studs while the other depicts hunting scenes and has the dog's name, Tantanuit, engraved on it. These are two of the best examples of the kind of ornate work which went into dog collars in ancient Egypt. By the time of the New Kingdom, in fact, the dog collar was its own type of artwork and worthy to be worn in the afterlife in the presence of the gods.
Life & the Afterlife in Egypt
During the period of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt (2040-1782 BCE) there was a significant philosophical shift where people questioned the reality of this paradise and emphasized making the most of life because nothing existed after death. Some scholars have speculated that this belief came about because of the turmoil of the First Intermediate Period which came before the Middle Kingdom, but there is no convincing evidence of this.
Such theories are always based on the claim that the First Intermediate Period of Egypt was a dark time of chaos and confusion which it most certainly was not. The Egyptians always emphasized living life to its fullest - their entire culture is based on gratitude for life, enjoying life, loving every moment of life - so an emphasis on this was nothing new. What makes the Middle Kingdom belief so interesting, however, is its denial of immortality in an effort to make one's present life even more precious.
The literature of the Middle Kingdom expresses a lack of belief in the traditional view of paradise because people in the Middle Kingdom were more 'cosmopolitan' than in earlier times and were most likely attempting to distance themselves from what they saw as 'superstition'. The First Intermediate Period had elevated the different districts of Egypt, made their individual artistic expressions as valuable as the state-mandated art and literature of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, and people felt freer to express their personal opinions rather than just repeat what they had been told. This skepticism disappears during the time of the New Kingdom, and - for the most part - the belief in the paradise of the Field of Reeds was constant throughout Egypt's history. A component of this belief was the importance of grave goods which would serve the deceased in the afterlife just as well as they had on the earthly plane.






