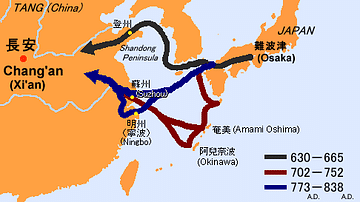
Ancient China was often connected to the rest of the world through trade, not only along the famous Silk Road but also via merchant ships that sailed the Indian Ocean, connecting East Asia to the Middle East, Europe, and Africa. Silk, paper, tea, and porcelain were just some of the goods the Chinese exported far and wide. Trade routes, once firmly established, also carried ideas and innovations as well as goods for sale.
In this collection of resources, we examine in detail the myriad of routes that connected the ancient empires and the Chinese goods that were most esteemed, from jade masks to fine lacquerware.
By the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE), tea had spread beyond the monasteries and become a popular drink with the gentry who were the only people who could afford such an expensive drink. Tea became an important element of the economy, with large estates in southeast China cultivating the plant and providing the government with valuable tax revenue on its sale.