Illustration
Throughout the study of the past, historians have relied on broad conceptual shortcuts to categorize time, societies, and developments. While these models help structure historical analysis and provide useful comparisons, they can oversimplify complex realities, impose artificial divisions, and reflect the biases of those who created them.
- Agricultural Revolution: The transition from hunting and gathering to settled farming, marking the foundation of modern civilization.
- The Three-Age System: A classification of prehistory into the Stone, Bronze, and Iron Ages, based on technological advancements.
- Indo-European Language Model: A linguistic classification grouping languages like Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit based on a common ancestral language.
- Byzantine Empire: A later term for the eastern half of the Roman Empire, highlighting its distinct cultural and religious development.
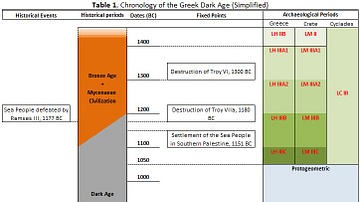
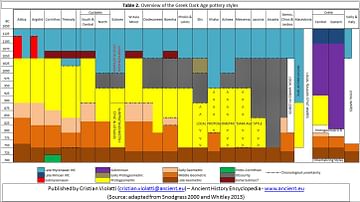
- The Dark Ages (Middle Ages): A term describing the period between the fall of Rome and the Renaissance, often viewed as a time of stagnation in Europe.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2025, March 07). 5 Terms of Convenience in History. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/20110/5-terms-of-convenience-in-history/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "5 Terms of Convenience in History." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified March 07, 2025. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/20110/5-terms-of-convenience-in-history/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "5 Terms of Convenience in History." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 07 Mar 2025, https://www.worldhistory.org/image/20110/5-terms-of-convenience-in-history/. Web. 05 Jul 2025.