Server Costs Fundraiser 2024
Illustration
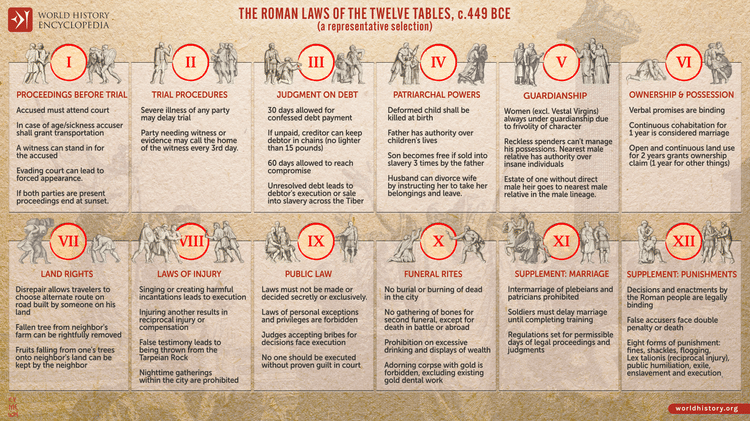
An infographic illustrating The Laws of the Twelve Tables were a set of ancient Roman laws put together and displayed in public around 450 BCE. These laws formed the core of the Roman legal system and provided a written code of conduct and regulations for various aspects of Roman society. The Twelve Tables covered multiple topics, including civil, criminal, and procedural laws, property rights, marriage and family law, and rules regarding debt and contracts. They aimed to establish legal equality among Roman citizens and ensure transparency and predictability in legal matters. The Laws of the Twelve Tables had a lasting influence on Roman law and became the foundation of the Western legal systems.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2023, June 02). The Roman Laws of the Twelve Tables, c. 449 BCE. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/17482/the-roman-laws-of-the-twelve-tables-c-449-bce/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Roman Laws of the Twelve Tables, c. 449 BCE." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified June 02, 2023. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/17482/the-roman-laws-of-the-twelve-tables-c-449-bce/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Roman Laws of the Twelve Tables, c. 449 BCE." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 02 Jun 2023. Web. 26 Jul 2024.