Search
Search Results

Article
Napoleonic Concordat of 1801 & Religious Pluralism
The Napoleonic Concordat of 1801 defined France's relationship with the Catholic Church for over 100 years. The Organic Articles were added in 1802 and provided state recognition of the Reformed and Lutheran confessions alongside the Catholic...
Article
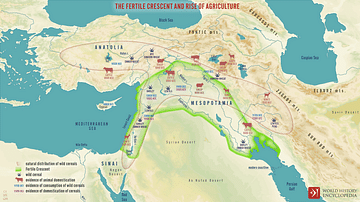
Dynamics of the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution began between 10,000 and 12,000 years ago at several widely dispersed locations across the world, when our ancestors first began planting and raising crops. Agricultural communities sprang up almost simultaneously...

Definition
Ceide Fields
The Ceide Fields, near Ballycastle, Co. Mayo, on the western coast of Ireland, are recognised as one of the oldest and largest Stone Age farming sites in the world, dating back to c. 3700 BCE. The walls that have been discovered so far, rest...

Article
Agriculture in the British Industrial Revolution
Agriculture, like most other areas of working life, was greatly affected by the machines invented during the Industrial Revolution. Agriculture in Britain and elsewhere had made leaps forward in the 18th century, and its success released...

Article
Origins of World Agriculture
Agriculture arose independently at several locations across the world, beginning about 12,000 years ago. The first crops and livestock were domesticated in six rather diffuse areas including the Near East, China, Southeast Asia, and Africa...

Definition
Stone Age
From the dawn of our species to the present day, stone-made artefacts are the dominant form of material remains that have survived to today concerning human technology. The term “Stone Age” was coined in the late 19th century...

Definition
Germ Theory
The germ theory, which emerged in the late 19th century, demonstrated that microscopic germs caused most human infectious diseases. The germs involved included bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and prions. Louis Pasteur (1822-1895), a French...
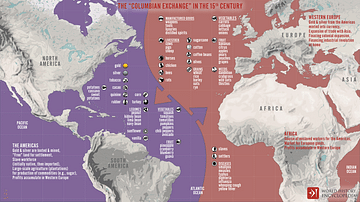
Definition
Columbian Exchange
The Columbian exchange is a term coined by Alfred Crosby Jr. in 1972 that is traditionally defined as the transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the Old World of Europe and Africa and the New World of the Americas. The exchange...

Article
Inca Food & Agriculture
The Inca empire controlled four climate zones and, consequently, their agricultural produce was diverse. Ancient Andean people were largely vegetarian, supplementing their diet with camelid meat and seafood if they could. The Incas developed...

Article
Viking Age Greenland
Greenland was drawn into the Viking Age and settled by Norse Vikings in the late 980s CE, their presence there lasting into the 15th century CE. Despite its ice-riddled geography, the Norse managed to carve out a living for themselves in...