Illustration
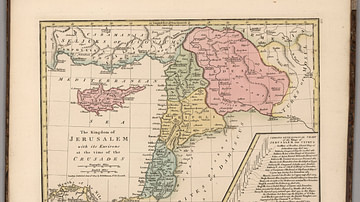
This map illustrates the Crusader States, or Outremer (from the Old French outre-mer, meaning "overseas"), in the 12th century, established following the First Crusade (1096–1099) and expanded through subsequent campaigns such as the Second (1147–1148) and Third Crusades (1187–1192). At their height, these Latin Christian realms—most notably the Kingdom of Jerusalem (1099–1187), Principality of Antioch (1098–1144), and County of Edessa (1098–1144)—spanned across the Levantine coast, parts of Anatolia, and Cyprus.
Formed amidst complex conflicts between Western crusaders, the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire (395–1453), and Muslim dynasties like the Zengids (1127–1183), Ayyubids (after 1171), and Seljuks (1037–1194), these states were fortified networks of cities, castles, and military roads. Major strongholds such as Krak des Chevaliers, Chastel Rouge, and Chastel Pelerin played key roles in defense and supply. The map also shows late Christian strongholds that persisted after the fall of Acre in 1291, marking the final retreat of crusader control from the Holy Land.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2025, June 13). Map of 12th-Century Crusader States (Outremer). World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/20583/map-of-12th-century-crusader-states-outremer/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "Map of 12th-Century Crusader States (Outremer)." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified June 13, 2025. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/20583/map-of-12th-century-crusader-states-outremer/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "Map of 12th-Century Crusader States (Outremer)." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 13 Jun 2025, https://www.worldhistory.org/image/20583/map-of-12th-century-crusader-states-outremer/. Web. 30 Jul 2025.