
Abacus - a large slab placed above the column capital to support the architrave or an arch placed above it.
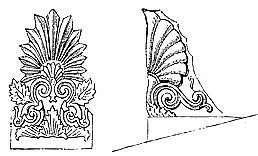
Akroterion - a decorative piece added to the roof of a temple at the apex and corners, usually made of clay or bronze and often in the form of a palm or statue, for example of Nike.

Adyton - the most sacred inner part of a temple, usually at the end of the cella furthest from the entrance, often with restricted access to the initiated or priests.

Aedicule - a frame formed by two columns and an entablature with pediment.
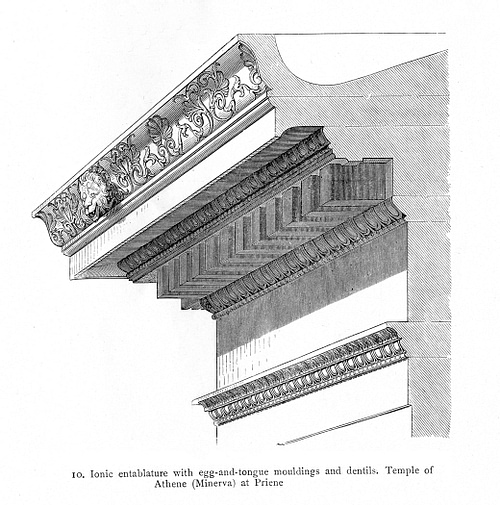
Architrave - the lowest part of the entablature, the part below the frieze.

Amphiprostyle Temple - when both façades have columns, e.g.: the temple of Nike, Athens.

Atlantide - a sculpted male figure acting as a column to support an entablature, named after Atlas.

Attic Story - the part placed above the entablature of a building, e.g.: often seen in triumphal arches.

Buttress - a mass placed to support a wall, especially when the wall bears an arch or heavy weight. Flying buttresses support a weight over space and allow for walls to be weakened by the inclusion of niches and windows.

Capital - the crown which joins the top of a column with the abacus and aids in distributing weight. Different types include the simple convex Doric and the highly decorative Corinthian with stylized acanthus leaves.

Caryatid - a sculpted female figure acting as a column to support an entablature, e.g.: in the Erechtheion.

Cavea - the seated area of a theatre, usually built into a natural slope.

Cella - the inner area of a temple, usually rectangular and without windows, sometimes columned. Often subdivided into smaller rooms, the largest of which often housed a large cult statue to a particular deity.

Column - used to support the abacus and architrave without the necessity of a wall. There are several types including the simple and earliest the Doric. They may also be free-standing and often commemorate significant historical events such as Trajan's Column.
Conch - also known as an apse, a recess in a wall often highly decorated or containing a statue.

Cornice - the decorative projecting part at the top of the entablature which also aided in drainage of rainwater.

Crepidoma - also crēpis, the three steps on which stand the columns of a temple. The final top step is known as the stylobate.

Decastyle Temple - with ten columns at each façade, e.g.: the temple of Apollo Didymaeus at Miletus.

Dentils - a regular series of squares or rectangles used to decorate cornices.

Diazoma - the walkway which horizontally divides the seats in a theatre.
Dipteral Temple - when there are a double row of columns on all sides, e.g.: the Parthenon.
Dodecastyle Temple - with twelve columns at each façade.

Dromos - the monumental unroofed and walled entrance to a tomb, e.g. at Mycenae.

Drum - the individual circular pieces used to construct some types of columns.

Egg and Dart Ornamentation - a typical feature of decoration on cornices.

Engaged Columns - columns which are incorporated within a wall.

Entablature - the structure which lies horizontally above columns and which is composed of the architrave, frieze and cornice.

Entasis - the swelling of a column at its base and centre to give the illusion of being perfectly straight.

Flute - the curved vertical channel carved in a column.

Frieze - the widest and central part of the entablature often richly decorated with relief sculpture.

Hexastyle Temple - with six columns at each façade, e.g. the Maison Carré at Nimes.

in antis - when the walls of a portico extend in line with the façade columns.

Intrados - the inner surface of an arch.

Metope - a square space in the frieze between two triglyphs, often filled with relief sculpture or ornaments such as shields.

Monolithic Column - a column carved from a single piece of stone.

Octastyle Temple - with eight columns at each façade, e.g.: the temple of Bacchus at Baalbek.
Opisthodomos - The small room at the rear of a temple commonly used as a treasury.

Parodoi - the large arched gateways, either side of the skēnē, through which an audience entered a theatre.

Pedestal - the block on which stands a column or statue, composed of the plinth, torus, dado and fascia.

Pediment - the triangular space above the entablature at the short sides of a temple. Often richly decorated with sculpture in the round.

Peripteral Temple - when all four external sides have columns.

Peristyle - the rows of columns which surround a temple or courtyard.

Pilaster - an ornamental column carved in relief on a wall surface.

Portico - a space for walking, usually columned, e.g.: at the front of a temple.

Pronaos - the space between the outer columns and cella entrance in a temple.

Propylon - the monumental gateway to a religious sanctuary or defined space. Often incorporating several separate entrances (propylaia).

Prostyle - a temple with columns only at the front façade.
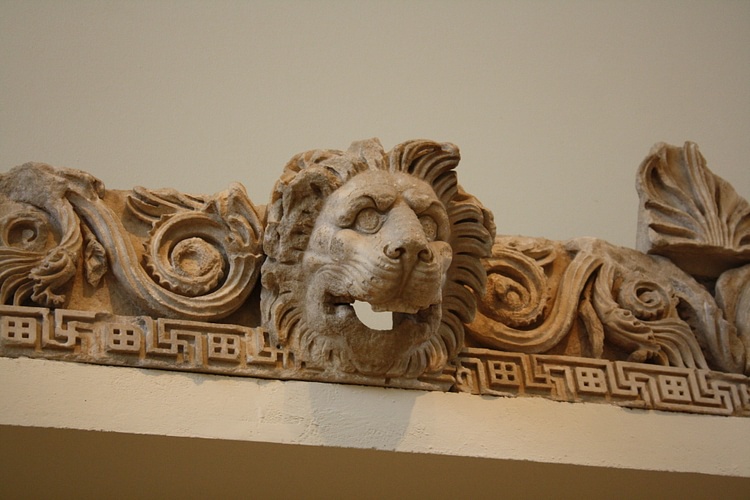

Sima - the gutter which collected rainwater from the roof of a temple, often containing decorative spouts at regular intervals.
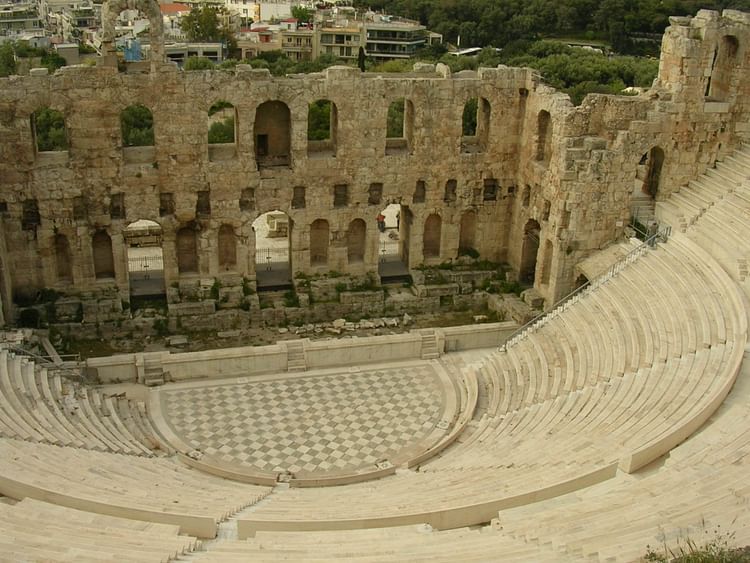

Skēnē - the background on a theatre stage, later examples were monumental in design.

Stereobate - the surface on which the stylobate stands.
Stoa - a long and narrow columned building often used to enclose a particular space at religious sites and public places such as markets and gymnasia. Used as a meeting place and shelter from the weather.
Stylobate - the foundation on which a row of columns stand. Often slightly curved to aid drainage.
Tetrastyle Temple - with four columns at each façade.
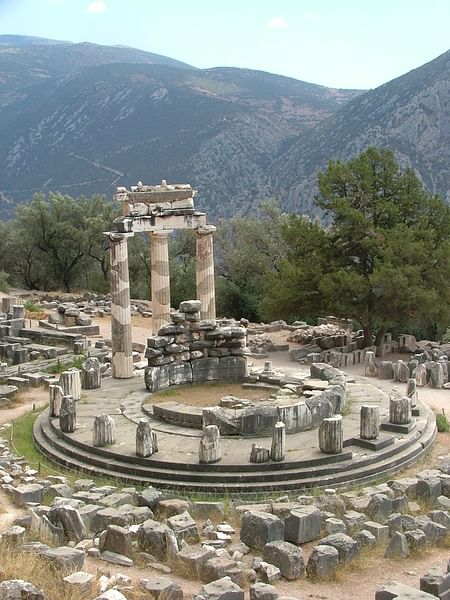

Tholos - A circular-shaped temple, the most famous example being at Delphi.
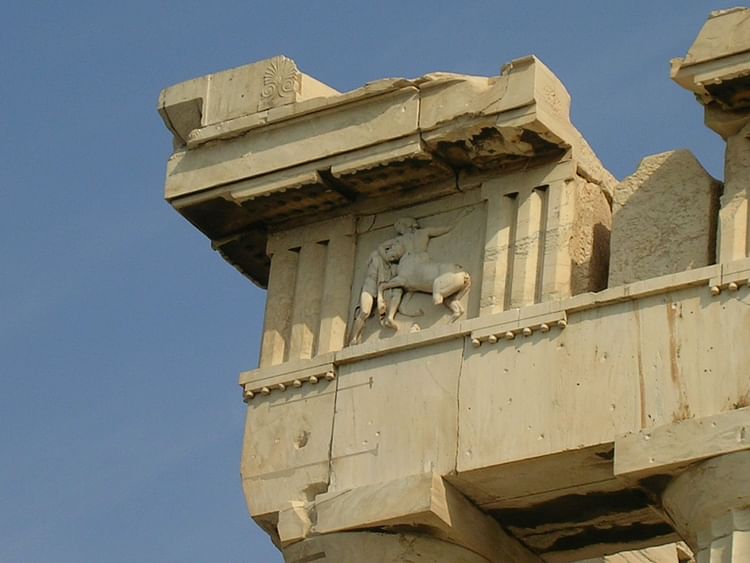

Triglyph - a decorative element of a frieze with two vertical grooves. Often used in alteration with metopes.

Triumphal Arch - a monumental archway to commemorate Roman military victories and other significant events.

Volutes - the scrolls of an Ionic capital.





