
Alure (Wall Walk)
The walkway along the higher and interior part of a wall which often gives access to the higher floors of towers within the wall. Typically protected by battlements.
Apse
A semicircular projecting part of a building, usually vaulted.

Arcade
An area of columned arches.

Arrow Loop
The narrow window of a wall or tower through which arrows and crossbow bolts could be fired. Usually a vertical slit, sometimes with a short horizontal slit to improve sighting.
Ashlar
Regular-shaped blocks of dressed masonry set in even horizontal rows.

Bailey (Ward)
The courtyard of a castle containing the principal buildings, including sometimes a tower keep, which may be surrounded by its own fortified wall.

Ballista
A large, fixed crossbow which fired large wooden bolts or iron-headed bolts. Used by both attackers and defenders.

Barbican
A short stretch of fortification outside the castle, especially used to provide extra protection for gates.

Barrel Vault
An arched vault between two walls.
Bartizan
A turret which overhangs the wall below. Common at the juncture of two walls, they provide extra defensive visibility.

Bastion
An angular projection from a curtain wall which gives an improved range of defensive fire.

Batter
The angled additional base to a wall or tower which increases the difficulty in climbing or dismantling the wall by attackers. See Talus.

Battlements
The crenellated top row of stones on a wall or tower. The merlons (raised section) and crenets (gaps) alternate to provide both cover and a line of fire for defenders.

Belfry
A mobile siege tower used to attack castles but sometimes also used by defenders.
Berm
The narrow area between the outer wall and its protective ditch or moat.

Blind Arcade
A row of false arches added to decorate a wall.
Boss (Keystone)
The central stone in a vault, often with decorative carving.
Burgus
An area of settlement connected to a castle by encircling earthworks.
Buttery
A room used to store drinks, especially wine, beer, and ale.
Buttress
A stone support of a wall, needed when the wall carries a roof or vault, or to provide extra defensive stability against dismantling or bombardment by attackers.
Chamber
A private room in a castle, for example, a bedroom.
Chemise
A wall which closely surrounds a keep.
Cistern
A tank for capturing rainwater and/or storing water.

Corbel
A stone which projects from a wall to support a roof timber or stone arch.
Countermine
A mine dug by the defenders in order to intersect and/or collapse the mine of the attackers.
Counterscarp
The outer slope of a ditch or moat.
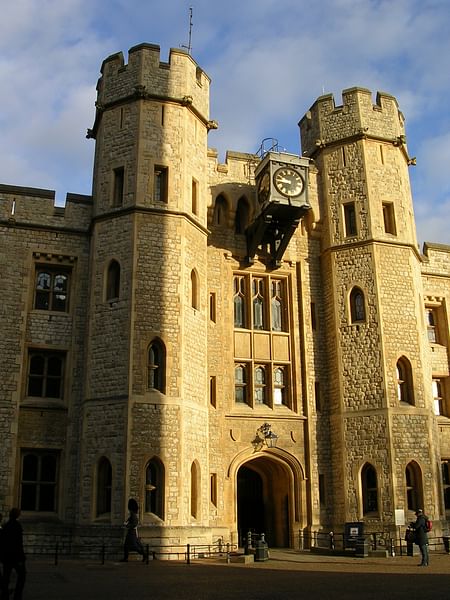

Crenellations
The top row of stones on a wall or tower which alternate between merlons (raised sections) and crenets (gaps) to provide both cover and a line of fire for defenders.

Crenet (Embrasure)
The gap between raised sections (merlons) in the battlements of a wall or tower.
Cruck
The curved timber which is set in the ground to support a roof or wall.

Curtain Wall
The outer wall of a castle.
Demesne
The lands owned by and farmed in the name of the castle owner but which were not usually leased.

Donjon
The medieval name for a tower keep.
Drawbar
The large horizontal beam of wood used to lock a gate.
Drawbridge
A short hinged bridge which can be raised to block a gateway or lowered to cover a section of the moat. Usually operated via a chain and winch.

Drum Tower
A round tower set within a curtain wall.

Earthworks
Raised areas of earth on which palisades and walls were built in early castles. May also refer in general to such defensive structures as moats.
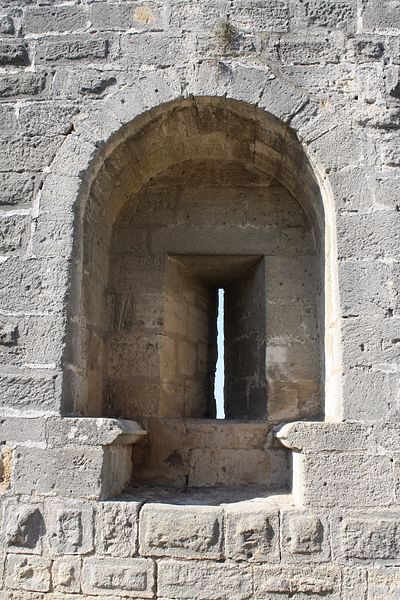

Embrasure
The splayed opening in a wall for an arrow loop or ordinary window which gives a defender room to stand and manoeuvre. Also an alternative name for a crenet.

Enceinte
The area enclosed by a fortified wall of a castle or town.
Fictive Masonry
The lines painted on a wall to make it resemble ashlar masonry. Often used on chamber interiors using red paint.

Forebuilding
The structure immediately in front of the tower keep which protects its entrance.
Gable
The triangular section of a wall between the sloping roofs of two adjoining buildings.
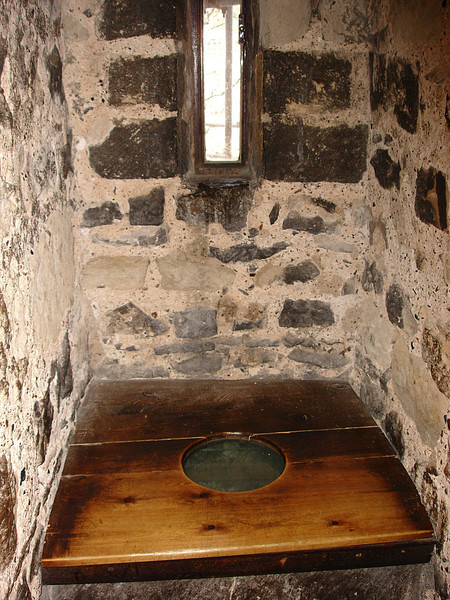

Garderobe
Another name for the latrine or toilet.

Gatehouse
The structure which developed to better protect gates, eventually having twin round towers and other defences like a drawbridge and portcullis.
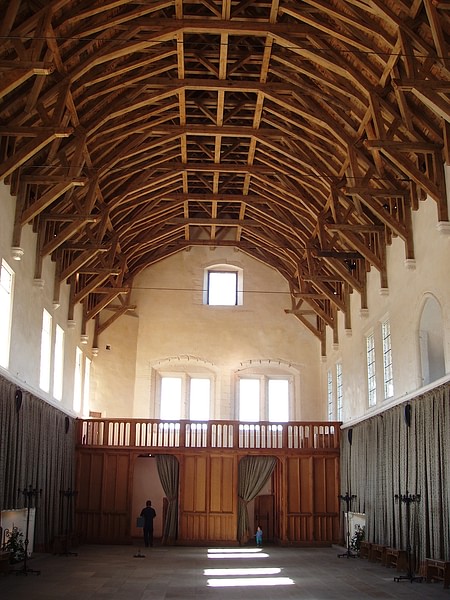

Great Hall
The main reception and dining room of the castle. Usually with an impressive beam or vaulted ceiling and enormous fireplace.

Hall Keep
A keep which does not have the height of a tower keep.

Hoardings
Wooden structures added to the top of walls and towers to provide a covered walkway and a secure place for defensive fire. Sometimes they could be removed during peacetime.

Keep
The term used from the 16th century CE to describe the main residential building of a castle. Known also as a great tower or donjon. They may be of only a few stories (Hall Keep) or four or more floors (Tower Keep).
Keystone (Boss)
The central stone in a vault, often with decorative carving.

Latrine
Toilet or garderobe, usually with a waste shaft emptying directly outside the walls.
Lintel
The large horizontal stone or beam above a doorway or window.
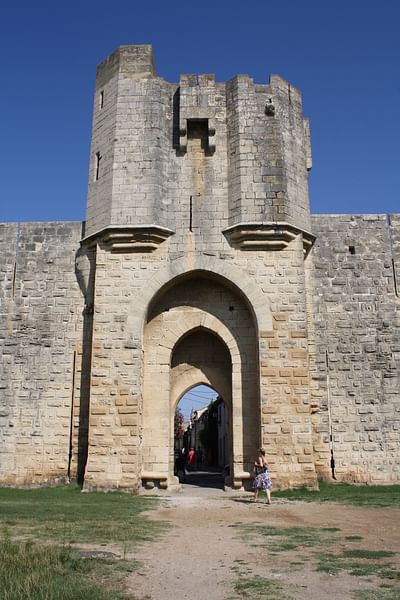

Machicolation (Murder Hole)
A hole in the projecting overhang of a wall or tower through which missiles may be dropped on the enemy and through which the base of the wall can be monitored.
Mangonel
A stone-throwing catapult which was powered by the torsion of ropes. Used by both defenders and attackers.

Merlon
The raised section which alternates with crenets (gaps) in the battlements of a wall or tower.
Mine
A tunnel dug under a castle by attackers to cause a partial collapse of it.

Moat
A ditch which encircles or partially encircles a castle's walls. They may be dry or filled with water (temporarily or permanently) and have wooden stakes driven into their sides to make them more slippery and so more difficult to climb by attackers.
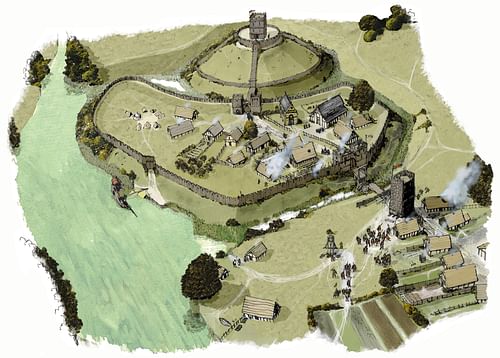
Motte & Bailey Castle
An early type of castle with an artificial or natural mound (motte) on which a tower is built with a courtyard (bailey) below, surrounded by a palisade and moat.

Mural Tower
A tower built into a curtain wall.
Mural Chamber
A small vaulted room built within a castle wall.

Mural Passage
A vaulted passageway which is built within the wall itself.
Murder Hole (Machicolation)
A hole in the projecting overhang of a wall or tower through which missiles may be dropped on the enemy and through which the base of the wall can be monitored.

Outworks
Those defensive arrangements outside the castle walls proper, for example, a moat or barbican.
Palisade
A wooden defensive wall.
Pantry
A room used to store food, especially bread, usually located near the Great Hall.
Parados
The low inner wall of a wall walk or alure.
Parapet
The raised top part of a wall, often with battlements, which offers some protection to defenders on the wall walk behind it.
Plinth
The lower projecting part of a wall or tower.

Portcullis
A grill made from wood, iron covered wood or purely iron which has a spiked base and is lowered to block a gate entrance. Usually raised and lowered via a chain and winch.
Postern Gate (Sally Port)
A small gate for pedestrians only which was used as a secondary entrance or emergency exit.
Rampart
An earth bank.
Ravelin
A triangular fortification structure set outside the curtain walls.
Rendering
The plaster covering of a stone wall, often lime-washed.
Revetment
A wooden or stone wall to protect one side of a moat or ditch.
Ringwork
An oval or circular earthwork with a bank and ditch which encloses domestic or other buildings.
Sally Port (Postern Gate)
A small gate for pedestrians only which was used as a secondary entrance or emergency exit.
Scarp
The inner slope of a ditch or moat or the edge of the earth platform on which a castle may be built to increase its height.
Screens Passage
The passageway which leads from the Great Hall to the service area.

Shell Keep
When the keep is built on an artificial or natural mound (motte) and surrounded by a stone circuit wall on the mound itself.
Solar Room
A private chamber within a tower keep, usually a high floor but of uncertain use.

Talus
The massive angled additional base to a wall or tower which increased the difficulty in climbing and dismantling the wall by attackers. Larger than a batter.
Tiltyard
The area used by knights to practise jousting, tilt being the wooden barrier which separates horsemen as they charge at each other.

Tower Keep
The main residential building of a castle consisting of many floors.
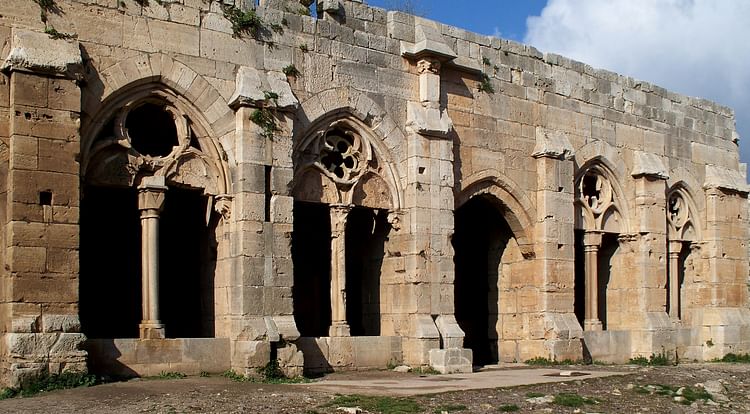

Tracery
Decorative patterned wood or stonework in a window frame.

Trebuchet
A stone-throwing catapult which was powered by a counterweight. Used by both defenders and attackers, it was more accurate and had a greater range than the mangonel.
Turning Bridge
An alternative to a drawbridge which swings on a central pivot so that the rear end lowers into a ditch or pit.

Turret
A small tower, sometimes added to the corners of a tower keep.

Vault
An arched ceiling made of stone.
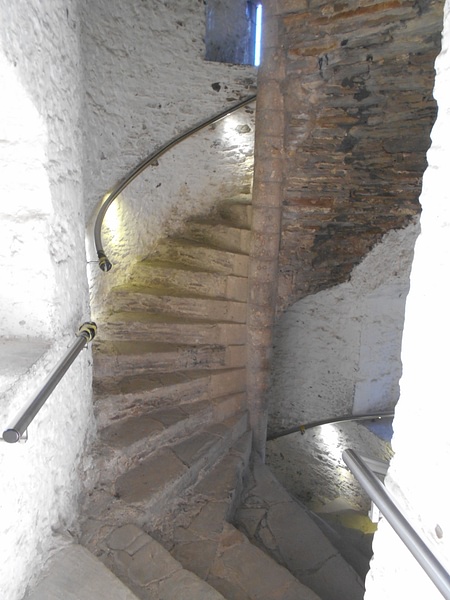

Vice
A spiral staircase.
Wall Walk (Alure)
The walkway along the higher and interior part of a wall which often gives access to the higher floors of towers within the wall.

Ward (Bailey)
The courtyard of a castle containing the principal buildings, including sometimes a tower keep, which may be surrounded by its own fortified wall.
Wattle & Daub
The combination of clay or earth (daub) with a strengthening latticework of wood (wattle) which was used in buildings instead of more expensive stone. In a motte and bailey castle, the interior buildings would have been mostly of wattle and daub.

Window Seat
A seat set into the wall by a window which provides good light for such activities as reading and embroidery.

Wing-wall
A fortification wall that descends into a moat.





