Search
Search Results

Definition
Edmond Halley
Edmond Halley (1656-1742) was an English astronomer, mathematician, and cartographer. Halley's Comet is named after him since he accurately predicted its return in 1758. One of the early globetrotting scientists, Halley led several maritime...

Definition
Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution (1500-1700), which occurred first in Europe before spreading worldwide, witnessed a new approach to knowledge gathering – the scientific method – which utilised new technologies like the telescope to observe, measure...

Image
Newton Commemorative Medal
A gilded commemorative medal showing the mathematician and physicist Isaac Newton (1642-1727). Made in England in 1726. (Science Museum, London)
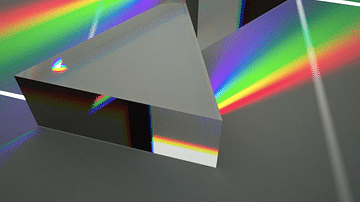
Image
Newton's Prism
Two prisms illustrating the discovery by Isaac Newton (1642-1727) that a single beam of white light could be split into a spectrum of colours, each colour being refracted at a slightly different angle from the other.

Image
Newton's Copy of Principia
The personal copy of Isaac Newton's (1642-1727) own work Principia in which he outlines his three laws of motion and universal law of gravity. (Wren Library, Trinity College, Cambridge)

Image
Newton's Reflecting Telescope
A replica of the reflecting telescope invented and designed by Isaac Newton (1642-1727) in 1668. 160 mm x 275 mm x 295 mm. (Science Museum, London)

Definition
Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens (1629-1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, and astronomer. A leading figure of the Scientific Revolution, Huygens combined research into mathematical-based theories, such as the movement of light waves, with practical...

Definition
Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon (1561-1626) was an English philosopher, statesman, and author. Bacon is often considered one of the founders of modern scientific research and scientific method, even as "the father of modern science" since he proposed a new...

Article
Clocks in the Scientific Revolution
Keeping good time proved an elusive objective for centuries, and it was only in the second half of the 17th century, during the Scientific Revolution (1500-1700), that clocks were made which lost seconds rather than minutes each day. The...

Definition
Constantine X Doukas
Constantine X Doukas was the ruler of the Byzantine Empire from 1059 to 1067 CE. During his reign, the Byzantine Empire was attacked by emerging enemies on all sides, including the Normans in Italy and the Seljuk Turks in Armenia and Anatolia...