Illustration
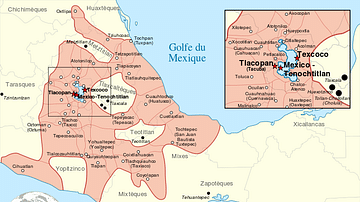
This map illustrates the origins and territorial expansion of the Aztec Empire in Mesoamerica between the 14th and 16th centuries. Emerging from a network of Nahua-speaking city-states in central and southern Mexico, the empire rose to dominate the region through military conquest, strategic alliances, and a tribute-based system centered on its capital, Tenochtitlán.
The Aztecs trace their origins to the 12th century, when they began settling in the Valley of Mexico among other competing city-states. By the 15th century, their empire had grown into the most powerful polity in Mesoamerica, rivaled only by the Inca Empire in South America. At its peak, the Aztec Triple Alliance—comprising Tenochtitlán, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan—controlled vast territories through a combination of warfare and diplomacy. Tenochtitlán, the capital (now Mexico City), was a thriving metropolis with a population exceeding 200,000. Following its conquest in the early 16th century by Spanish forces under Hernán Cortés, the city became the nucleus of the Viceroyalty of New Spain.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2021, June 03). Map of the Aztec Empire, c. 1427–1521. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/14181/map-of-the-aztec-empire-c-1427-1521/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "Map of the Aztec Empire, c. 1427–1521." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified June 03, 2021. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/14181/map-of-the-aztec-empire-c-1427-1521/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "Map of the Aztec Empire, c. 1427–1521." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 03 Jun 2021, https://www.worldhistory.org/image/14181/map-of-the-aztec-empire-c-1427-1521/. Web. 29 Jul 2025.