Search
Search Results
Image
The First Telegraph Machine
The first telegraph machine, invented in 1837 by William Fothergill Cook (1806-79) and Charles Wheatstone (1802-1875). The machine had only 20 letters, indicated in the message sent by the slight movement of two needles (from the machine’s...
Image
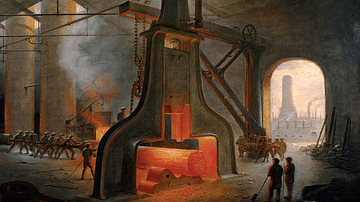
Nasmyth's Steam Hammer
An 1871 oil painting of a steam hammer invented by the Scotsman James Nasmyth (1808-1890) in 1839 during the Industrial Revolution. The steam-powered machine lowered a weight onto an anvil using gears which allowed for both precision and...

Image
Telegraph Morse Key
A morse key for an electrical telegraph machine. From a British post office and in use in the 19th to 20th century. (Science Museum, London)

Image
Eyepiece of Galileo's Telescope
The eyepiece of a model of the telescope made by Galileo (1564-1642) c. 1608. Galileo made a telescope capable of x33 magnification and used it to make several important discoveries in astronomy. 970 mm x 60 mm. (Science Museum, London)

Image
Newton's Reflecting Telescope
A replica of the reflecting telescope invented and designed by Isaac Newton (1642-1727) in 1668. 160 mm x 275 mm x 295 mm. (Science Museum, London)

Definition
Euclid
Euclid of Alexandria (lived c. 300 BCE) systematized ancient Greek and Near Eastern mathematics and geometry. He wrote The Elements, the most widely used mathematics and geometry textbook in history. Older books sometimes confuse him with...

Image
Robert Hooke Microscope
A microscope of the type invented by the English scientist Robert Hooke (1635-1703). Made between 1671 and 1700. The device on the left, designed by Hooke, is a scotoscope which helped better illuminate the specimen under view in the microscope...

Image
Persian Astrolabe
A brass planispheric astrolabe engraved with Arabic script. Probably Persian and dating to c. 1650. The astrolabe was a device used to measure the position of stars, time, and as a surveying tool. (Science Museum, London)

Article
Astronomy in the Scientific Revolution
The astronomers of the Scientific Revolution rejected long-held theories of ancient thinkers like Claudius Ptolemy and Aristotle and instead set out to systematically observe the heavens in order to create a model of the universe that fit...

Image
Making Steel by Skinner
A 1917 oil on canvas painting by E.F. Skinner showing steel being made using a Bessemer converter, an invention of the Industrial Revolution. (Science Museum, London)