Search
Search Results

Definition
David Hume
David Hume (1711-1776) was a Scottish philosopher, writer, historian, and important figure in the Enlightenment. Hume presented a positive view of human nature but a sceptical view of religion's usefulness. His Treatise of Human Nature was...

Definition
The Enlightenment
The Enlightenment (Age of Reason) was a revolution in thought in Europe and North America from the late 17th century to the late 18th century. The Enlightenment involved new approaches in philosophy, science, and politics. Above all, the...

Definition
Yomi
Yomi, or Yomi-tsu-kuni, is the underworld of the Shinto religion, even if it forms no part of Shinto theology and appears only in ancient myths as told in the 8th-century CE Kojiki, notably the story of the creator gods Izanami and Izanagi...

Definition
Adam Smith
Adam Smith (1723-1790) was a Scottish philosopher, economist, and leading Enlightenment figure. In The Wealth of Nations, he advocates free trade and limited interference in markets by governments, for which he is seen as the founder of liberal...

Definition
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) was a German Enlightenment thinker who is widely regarded as one of the most important philosophers of any period. His most famous works of critical philosophy include The Critique of Pure Reason, which challenged...

Definition
Charvaka
Charvaka (also given as Carvaka) was a philosophical school of thought, developed in India c. 600 BCE, stressing materialism as the means by which one understands and lives in the world. Materialism holds that perceivable matter is all that...

Definition
State of Nature
The state of nature is an idea which became especially popular with certain philosophers during the Enlightenment, notably Thomas Hobbes (1588-1679), John Locke (1632-1704), and Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778). It refers to a state of existence...

Definition
Utilitarianism
Utilitarianism is a philosophy founded by Jeremy Bentham (1748-1832) and then extended by other thinkers, notably John Stuart Mill (1806-1873). Utilitarianism involves the greatest happiness principle, which holds that a law or action is...

Definition
Jeremy Bentham
Jeremy Bentham (1748-1832) was an English philosopher and liberal social reformer best known as the founder of utilitarianism based on the greatest happiness principle, that is, rationally judging the success of a law by considering how many...
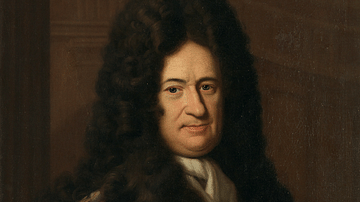
Definition
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646-1716) was a German polymath who became well-known across Europe for his work, particularly in the fields of science, mathematics, and philosophy. Leibniz's rationalist philosophy attempted to reconcile traditional...