Illustration
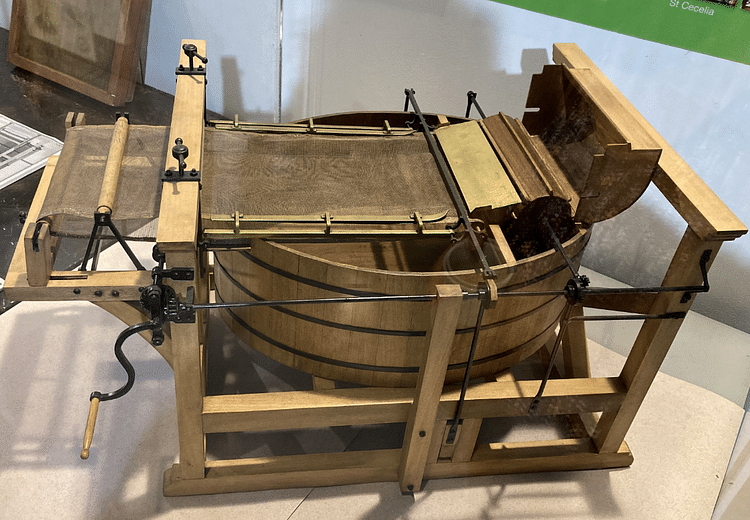
As with many inventions during the Industrial Revolution, the papermaking machine was something of a collaborative affair. This model is of one of the early machines developed by the Frenchman Nicholas Louis Robert (1761-1828) in 1799. The machine was further developed by John Gamble in England, who then collaborated with Henry (1766-1854) and Sealy Fourdrinier (1773-1847). This trio commissioned the engineer John Hall to build an improved papermaking machine, who, in turn, enlisted the help of his brother-in-law, Bryan Donkin (1768-1855).
By 1803, the end result of the collaboration was a machine that greatly speeded up paper production, a task previously done by hand, and, by saving on labour costs, it reduced the costs of books to make them more affordable to more people. The machine took a diluted pulp of linen pieces and water and spread them upon a mesh barrel. Water drained off and then the mash was placed between two layers of felt and pressed firmly between two rollers.
Frogmore Paper Mill, Apsley, Hertfordshire, UK.
Cite This Work
APA Style
Chris55, . (2023, April 19). Papermaking Machine. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/17305/papermaking-machine/
Chicago Style
Chris55, . "Papermaking Machine." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified April 19, 2023. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/17305/papermaking-machine/.
MLA Style
Chris55, . "Papermaking Machine." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 19 Apr 2023. Web. 24 Apr 2024.