Illustration
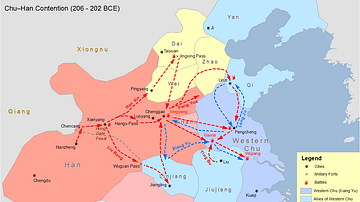
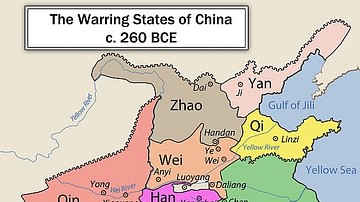
This map illustrates the Warring States period in Chinese history, a time of intense fragmentation and warfare spanning roughly from 475 BCE to 221 BCE. It marks the final centuries of the Zhou dynasty, during which its former vassal states declared independence and competed for supremacy, leading to the eventual unification of China under Qin rule.
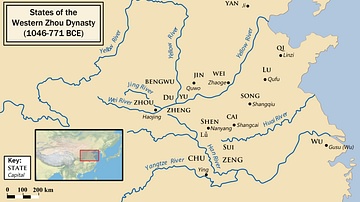
The Warring States period followed the decline of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (770 - 256 BCE), as regional lords turned into sovereign kings. Through relentless military campaigns, political alliances, and reforms, powerful states absorbed their weaker neighbors. By the 4th century BCE, seven dominant kingdoms remained: Qin, Chu, Zhao, Wei, Han, Yan, and Qi. Each pursued aggressive expansion and centralization. In 221 BCE, King Zheng of Qin (reign 247 - 221 BCE) succeeded in conquering all rival states, establishing the Qin dynasty (221 - 206 BCE) and becoming China’s first emperor, Qin Shi Huang. This period laid the foundations of imperial China and its enduring bureaucratic structure.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2022, July 08). Map of the Warring States of China & Qin Conquest. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/16124/map-of-the-warring-states-of-china--qin-conquest/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "Map of the Warring States of China & Qin Conquest." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified July 08, 2022. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/16124/map-of-the-warring-states-of-china--qin-conquest/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "Map of the Warring States of China & Qin Conquest." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 08 Jul 2022, https://www.worldhistory.org/image/16124/map-of-the-warring-states-of-china--qin-conquest/. Web. 30 Jul 2025.