Search
Search Results

Article
Lucius Cornelius Sulla: Guardian or Enemy of the Roman Republic?
For centuries, Lucius Cornelius Sulla has been reviled as a maniacal tyrant who defiled the Roman constitution and instituted bloody purges, but some modern historians assert that he has been judged too harshly. They present him as a republican...

Article
Continuity and Change after the Fall of the Roman Empire
The cataclysmic end of the Roman Empire in the West has tended to mask the underlying features of continuity. The map of Europe in the year 500 would have been unrecognizable to anyone living a hundred years earlier. Gone was the solid boundary...

Definition
Arthashastra
The Arthashastra is an Indian treatise on politics, economics, military strategy, the function of the state, and social organization attributed to the philosopher and Prime Minister Kautilya (also known as Chanakya, Vishnugupta, l. c. 350-275...

Definition
Medieval Icelandic Government
Early medieval Icelandic government, or Viking Iceland, has been termed an incipient form of democracy or democratic parliamentarism, however, the system was actually nothing like its European counterparts, be they medieval or contemporary...

Article
Prehistoric Hunter-Gatherer Societies
Hunter-gatherer societies are – true to their astoundingly descriptive name – cultures in which human beings obtain their food by hunting, fishing, scavenging, and gathering wild plants and other edibles. Although there are still groups of...

Article
Authority in Ancient Rome: Auctoritas, Potestas, Imperium, and the Paterfamilias
Authority in ancient Rome was complex, and as one can expect from Rome, full of tradition, myth, and awareness of their own storied history. Perhaps the ultimate authority was imperium, the power to command the Roman army. Potestas was legal...

Definition
State of Nature
The state of nature is an idea which became especially popular with certain philosophers during the Enlightenment, notably Thomas Hobbes (1588-1679), John Locke (1632-1704), and Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778). It refers to a state of existence...

Article
The Three Estates of Pre-Revolutionary France
Society in the Kingdom of France in the period of the Ancien Regime was broken up into three separate estates, or social classes: the clergy, the nobility, and the commoners. These classes and their accompanying power dynamics, originating...
Definition
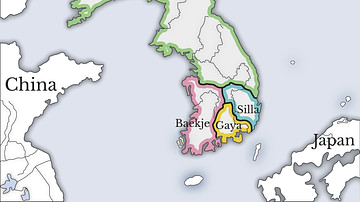
Three Kingdoms Period in Korea
The Three Kingdoms Period of ancient Korea (57 BCE – 668 CE) is so-called because it was dominated by the three kingdoms of Baekje (Paekche), Goguryeo (Koguryo), and Silla. There was also, though, a fourth entity, the Gaya (Kaya) confederation...

Definition
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire, at its height (c. 117), was the most extensive political and social structure in western civilization. Building upon the foundation laid by the Roman Republic, the empire became the largest and most powerful political and...