Search
Remove Ads
Advertisement
Summary 
Loading AI-generated summary based on World History Encyclopedia articles ...
Search Results

Article
Jesuit Influence on Post-medieval Chinese Astronomy
Ancient China had seen little Western contact before the 16th century CE, the language, culture and science all being allowed to develop independently of foreign influence. By the time European Jesuit missionaries arrived in the 16th century...
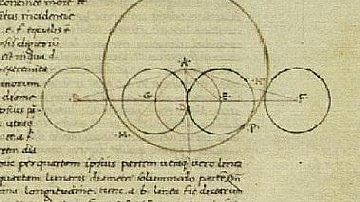
Definition
Greek Astronomy
Ancient Greek astronomy was the study of the universe to understand how it functioned and why apart from the established theistic model that claimed all things were ordered and maintained by the gods. Ancient Greek astronomers relied on observation...

Article
Astronomy in the Scientific Revolution
The astronomers of the Scientific Revolution rejected long-held theories of ancient thinkers like Claudius Ptolemy and Aristotle and instead set out to systematically observe the heavens in order to create a model of the universe that fit...

Article
The Athenian Calendar
The term “Athenian Calendar” (also called the “Attic Calendar”) has become somewhat of a misnomer, since Ancient Athenians never really used just one method to reckon the passage of time. Athenians, especially from the 3rd Century BCE forward...

Video
The History of Astronomy in the Ancient World
The history of astronomy in the Ancient World can be traced back thousands of years, and well before the Ancient Greek philosophers famously worked on it. It is generally agreed that the discipline of astronomy began in the region of Mesopotamia...
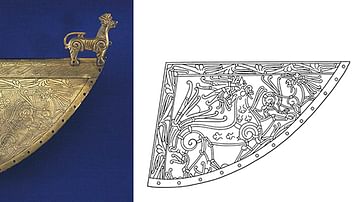
Image
The Heggen Weather Vane
This wind vane (Old Norse veðrviti) glittered at the prow of a longship in the 11th century. Such vanes are very decorative - here a motif of the great beast - and mark of high status in the Viking Age and Early Middle Ages, not only simple...

Image
Weather Vane in Ringerike Style
Copper-gilt weather vane from Söderala, Hälsingland, Sweden, dating to the Viking Age (c. 790-1100 CE). The style of its open-work pattern reminds of the Urnes style ornamentation, but the animal and its axial form place this vane firmly...

Definition
Hellenistic Astrology
Hellenistic astrology encompassed various forms of divination in Greece and the Mediterranean, all linked to the observation of astronomical phenomena. Hellenistic astrology was based on the belief that the stars and planets could either...
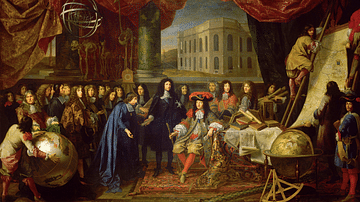
Article
Observatories in the Scientific Revolution
The foundation of observatories during the Scientific Revolution (1500-1700) followed a process of evolution from entirely independent observatories operated by a single astronomer to private observatories which received state or private...

Article
The Hellenistic World: The World of Alexander the Great
The Hellenistic World (from the Greek word Hellas for Greece) is the known world after the conquests of Alexander the Great and corresponds roughly with the Hellenistic Period of ancient Greece, from 323 BCE (Alexander's death) to the annexation...